Ultimate Guide to Bicycle Geometry
Content:
- I. Introduction to Bicycle Geometry
- Definition of Bicycle Geometry
- Importance of Bicycle Geometry in Bike Fit and Performance
- Purpose of the Guide
- II. Essential Bicycle Geometry Measurements
- Frame Size
- Top Tube Length
- Reach
- Stack
- Seat Tube Angle
- Head Tube Angle
- Trail
- Fork Rake
- Explanation of each Measurement's Impact on Fit and Performance
- III. Different Bicycle Geometry Styles
- IV. Factors to Consider in Choosing Bicycle Geometry
- V. Conclusion
I. Introduction to Bicycle Geometry
Definition of Bicycle Geometry
Bicycle geometry is the set of measurements, angles, and shapes that define the design and construction of a bicycle. It encompasses all the key elements of a bike's frame and components, including the frame size, top tube length, head tube angle, seat tube angle, and chainstay length. These elements determine the fit, comfort, and performance of a bike and play a critical role in how a bike handles, rides, and feels. Bicycle geometry also takes into consideration the material and construction of the frame, which affects the strength, weight, and rigidity of the bike. In essence, bicycle geometry is the blueprint that defines the riding characteristics and qualities of a bicycle.
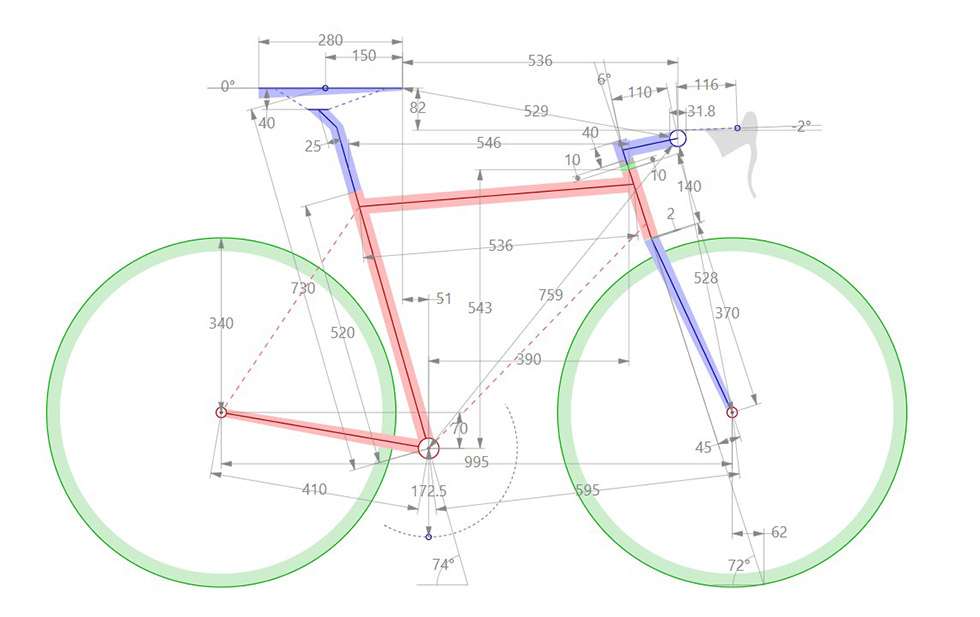
Importance of Bicycle Geometry in Bike Fit and Performance
The importance of bicycle geometry in bike fit and performance cannot be overstated. Bicycle geometry is the foundation on which the overall design and functionality of a bike is built. It affects every aspect of a bike's performance, from the rider's comfort and stability to the bike's handling and responsiveness.
In terms of fit, the right bicycle geometry is essential for ensuring that a bike is the right size for the rider. A correctly sized bike will allow the rider to reach the handlebars and pedals with ease, maintain a balanced and stable riding position, and prevent discomfort and injury. A bike that is too small or too large can lead to discomfort, fatigue, and even injury, making it difficult and unpleasant to ride.
Bicycle geometry also plays a crucial role in determining the performance of a bike. The head tube angle, for example, affects the bike's stability and handling, with a steep head tube angle providing quicker handling and a more upright riding position, and a slack head tube angle providing a more aggressive riding position and stability at high speeds. The chainstay length affects the bike's maneuverability and stability, with a longer chainstay providing more stability and a shorter chainstay providing more maneuverability.
The material and construction of the frame also play a role in the performance of a bike. A frame made from carbon fiber, for example, will be lighter and more rigid than a frame made from aluminum, while a frame made from titanium will be stronger and more durable. The method of construction used will also affect the performance of a bike, with different techniques providing different levels of stiffness and strength.
Bicycle geometry is an essential aspect of bike design that affects the fit, comfort, and performance of a bike. A well-designed bike with the right geometry will provide optimal performance, comfort, and stability, making it a joy to ride. On the other hand, a poorly designed bike with poor geometry will be difficult to ride, uncomfortable and potentially dangerous.
Purpose of the Guide
The purpose of this guide is to provide an introduction to bicycle geometry and it's importance in bike fit and performance. The guide aims to educate and inform riders of all levels, from beginners to experienced cyclists, about the key elements of bicycle geometry and how they affect the fit, comfort, and performance of a bike.
This guide will cover the basics of bicycle geometry, including the definitions of the key elements such as frame size, top tube length, head tube angle, seat tube angle, and chainstay length. It will also explain how each element affects the bike's fit, comfort, and performance. Additionally, the guide will provide information on the different materials used in bike construction and how they affect the performance and durability of a bike.
The goal of this guide is to provide riders with the knowledge and understanding they need to make informed decisions about the bikes they ride and the components they choose. Whether you're looking to purchase your first bike or upgrade to a higher-performance model, this guide will help you understand the key elements of bicycle geometry and how they impact the overall riding experience.
By the end of this guide, readers should have a better understanding of bicycle geometry and its importance in bike fit and performance. They will be equipped with the knowledge they need to choose the right bike and components for their needs and preferences, ensuring a comfortable and enjoyable riding experience.
II. Essential Bicycle Geometry Measurements
Frame Size
Bicycle frame size is one of the most important factors to consider when purchasing a bike. The frame size determines the overall size of the bike and has a significant impact on the fit, comfort, and performance of the bike. It is essential to choose the right frame size to ensure a comfortable and safe riding experience.
Frame size is typically measured in inches or centimeters and refers to the length of the seat tube, which is the part of the frame that the seat post and saddle are inserted into. The size of the frame can affect the height of the saddle, the reach to the handlebars, and the overall feel of the bike. A frame that is too small can result in discomfort, poor handling, and even injury, while a frame that is too large can lead to a feeling of being stretched out and unbalanced.
To determine the right frame size, you need to consider your body measurements and riding style. Your height and inseam length are the two most important factors to consider when choosing a frame size. However, other factors such as arm length, torso length, and riding style can also impact the fit and performance of the bike. For example, a person who wants to race their bike may prefer a smaller frame size for a more aggressive riding position, while a person who wants to use their bike for recreational purposes may prefer a larger frame size for a more comfortable and upright riding position.
It's also important to consider the type of bike you are looking to purchase when determining the right frame size. Different types of bikes, such as road bikes, mountain bikes, and city bikes, have different frame sizes and geometry, so it's essential to choose the right size based on the type of riding you plan to do.
In conclusion, choosing the right frame size is essential for ensuring a comfortable and safe riding experience. It's important to consider your body measurements and riding style when choosing a frame size, and to make sure you choose the right size based on the type of bike you are looking to purchase. With the right frame size, you can enjoy a smooth and comfortable riding experience, free from discomfort and injury.
Top Tube Length
The top tube length is one of the key elements of bicycle geometry that affects the fit and handling of a bike. The top tube length refers to the length of the bar that runs from the head tube to the seat tube of the bike. This element has a significant impact on the reach to the handlebars, the overall stability of the bike, and the rider's comfort.
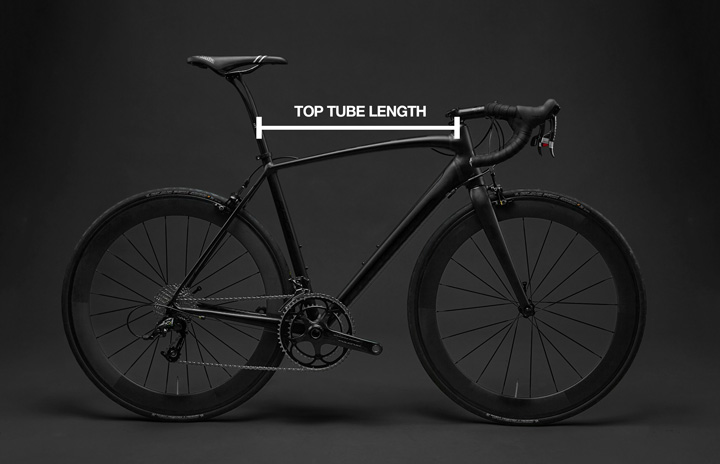

A longer top tube length can result in a longer reach to the handlebars, which is ideal for more aggressive riding positions and racing. On the other hand, a shorter top tube length can result in a shorter reach to the handlebars, which is ideal for more upright riding positions and recreational riding.
The top tube length is also closely related to the frame size of the bike. A larger frame size typically results in a longer top tube length, while a smaller frame size results in a shorter top tube length. However, this is not always the case, as different bike manufacturers may have their own unique geometry.
When choosing a bike, it's important to consider the top tube length, as it can have a significant impact on the fit and handling of the bike. The ideal top tube length for you will depend on your body measurements, riding style, and the type of riding you plan to do. For example, a road racer may prefer a longer top tube length for a more aggressive riding position, while a recreational rider may prefer a shorter top tube length for a more upright and comfortable riding position.
Additionally, it's important to note that the top tube length can also affect the overall stability of the bike. A longer top tube length can result in a less stable bike, while a shorter top tube length can result in a more stable bike. This is why it's essential to choose the right top tube length based on the type of riding you plan to do and your personal preferences.
In conclusion, the top tube length is a crucial element of bicycle geometry that affects the fit and handling of a bike. When choosing a bike, it's important to consider the top tube length, as well as your body measurements, riding style, and the type of riding you plan to do, to ensure that you choose the right top tube length for your needs. With the right top tube length, you can enjoy a smooth and comfortable riding experience, with optimal handling and stability.
Reach
Reach is a crucial aspect of bicycle geometry that refers to the distance between the saddle and the handlebars. It's one of the key factors that affects the fit and handling of a bike, and it has a significant impact on the overall comfort and performance of the rider.
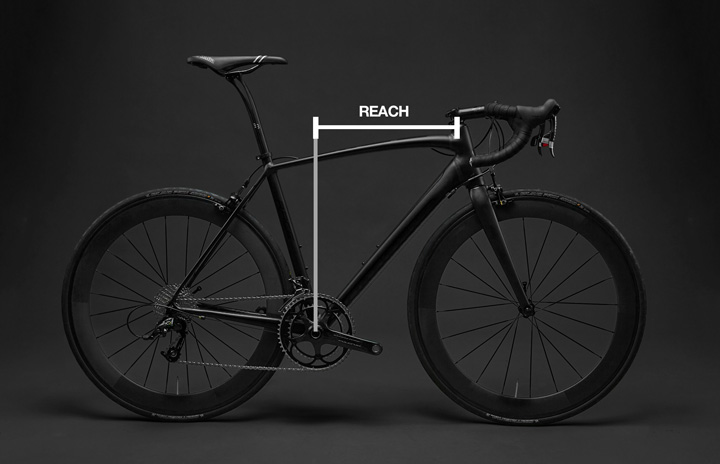

The reach determines how far the rider must stretch to reach the handlebars and is closely related to the top tube length, frame size, and stem length. A longer reach can result in a more aggressive riding position and improved aerodynamics, making it ideal for road racing and more aggressive riding styles. On the other hand, a shorter reach can result in a more upright and relaxed riding position, making it ideal for recreational riding and city riding.
Stack
Stack is a term used in bicycle geometry to describe the vertical distance between the center of the bottom bracket and the top of the head tube. It is a key aspect of bike fit that affects the rider's overall comfort and performance.
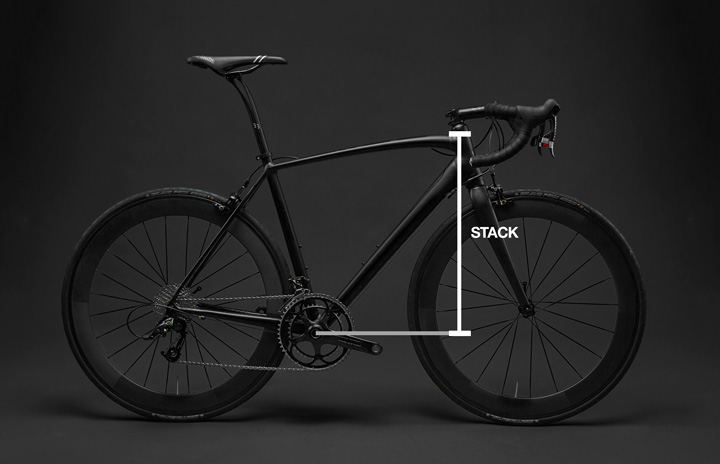

The stack height determines the rider's riding position and can impact their visibility, control, and aerodynamics. A higher stack height can result in a more upright riding position, while a lower stack height can result in a more aggressive riding position.
The ratio of stack to reach plays a crucial role in choosing the right bike, especially for road and racing disciplines where aerodynamics and efficiency are key. Professional bike fitting services often rely on stack to reach ratios to optimize comfort, power transfer, and aerodynamics. Riders who seek a balance between speed and comfort should carefully analyze these values to ensure the best possible fit for their specific needs.
Seat Tube Angle
The seat tube angle is an important aspect of a bicycle frame geometry that refers to the angle at which the seat tube, which houses the seat post and saddle, is positioned relative to the ground. This angle affects the rider's weight distribution on the bike and their position relative to the bottom bracket, which in turn impacts the handling and stability of the bike.
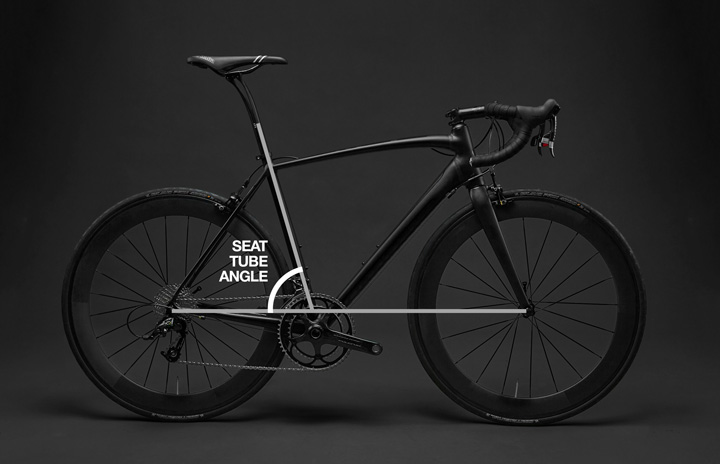

A steeper seat tube angle, typically around 73-75 degrees, brings the rider's weight forward and results in a more aggressive riding position, which is favored by road racers and other riders who prioritize speed and power over comfort. A shallower seat tube angle, around 69-71 degrees, places the rider's weight further back, making the bike more stable and comfortable for casual riding, touring, and other non-competitive applications.
Head Tube Angle
The head tube angle refers to the angle at which the head tube, which houses the fork and the front wheel, is positioned relative to the ground. Like the seat tube angle, the head tube angle affects the handling and stability of the bike.
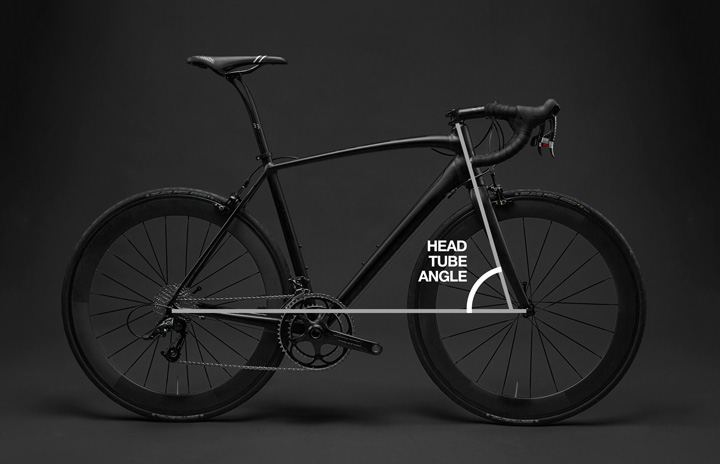

A steeper head tube angle, typically around 71-72 degrees, results in quicker handling and more responsive steering. This type of geometry is commonly found on road racing bikes, as well as some mountain bikes that prioritize agility and quick handling over stability.
A slacker head tube angle, around 68-69 degrees, provides more stability and a more relaxed, less twitchy ride. This type of geometry is commonly found on trail and enduro mountain bikes, as well as some touring bikes.
Trail
Trail is a term used in bicycle geometry to describe the horizontal distance between the front wheel's point of contact with the ground and the intersection of an imaginary line drawn through the center of the head tube and the ground. It plays a crucial role in the handling and stability of a bike.
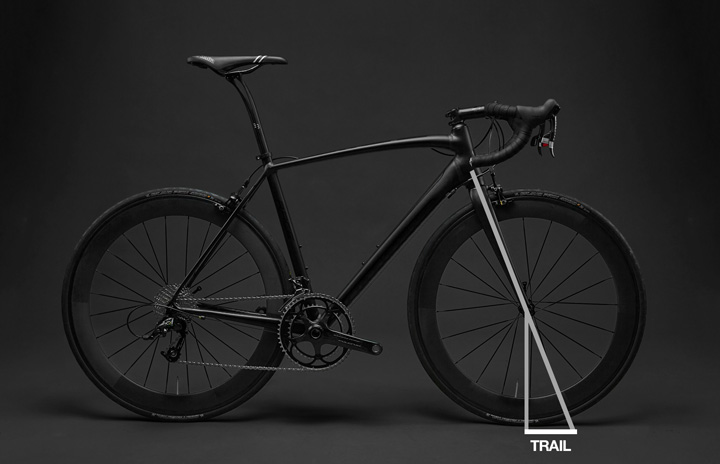

Trail affects how a bike handles and behaves when riding, and it is a trade-off between stability and agility. A bike with a higher trail will generally have better stability, while a bike with a lower trail will have better agility.
It's also important to note that the trail can be affected by the choice of tires, as well as the size and width of the tires. A bike with wider tires may have a different trail than a bike with narrower tires, and this can impact the handling and stability of the bike.
Fork Rake
Fork rake refers to the distance between the centerline of the fork blades and the centerline of the steer tube. This dimension affects the handling and stability of a bicycle, as well as the amount of trail the bike has.
A fork with more rake, or offset, will provide more trail, which helps to stabilize the bike at higher speeds and improves handling. Bikes with a more relaxed geometry, such as touring bikes or comfort bikes, often have more rake.
A fork with less rake will provide less trail and result in quicker handling, which is favored by racing bikes or bikes that prioritize agility.
Explanation of each Measurement's Impact on Fit and Performance
Each measurement of a bicycle frame geometry has a unique impact on fit and performance. Here's a more detailed explanation:
Seat tube angle: The seat tube angle affects the rider's weight distribution on the bike and their position relative to the bottom bracket, which in turn impacts the handling and stability of the bike. A steeper seat tube angle will bring the rider's weight forward, resulting in a more aggressive riding position, while a shallower seat tube angle will place the rider's weight further back, making the bike more stable and comfortable for casual riding.
Head tube angle: The head tube angle affects the handling and stability of the bike. A steeper head tube angle results in quicker handling and more responsive steering, while a slacker head tube angle provides more stability and a more relaxed, less twitchy ride.
Top tube length: The top tube length, or the distance between the head tube and the seat tube, affects the reach and the standover height of a bike. A longer top tube will result in a longer reach and a higher standover height, while a shorter top tube will result in a shorter reach and a lower standover height.
Chainstay length: The chainstay length, or the distance between the bottom bracket and the rear axle, affects the wheelbase of a bike. A longer chainstay length results in a longer wheelbase, which provides more stability, while a shorter chainstay length results in a shorter wheelbase, which provides more agility.
Fork rake: Fork rake affects the amount of trail the bike has, which in turn affects the handling and stability of the bike. A fork with more rake will provide more trail, which helps to stabilize the bike at higher speeds and improves handling, while a fork with less rake will provide less trail and result in quicker handling.
III. Different Bicycle Geometry Styles
Road Racing Geometry
Road racing geometry refers to the frame geometry of bicycles that are designed for road racing and high-speed, performance-oriented riding. The focus of road racing geometry is to provide a fast, efficient, and aggressive riding position that allows the rider to generate maximum power and speed.
Key characteristics of road racing geometry include:
- Steep seat tube angle: A seat tube angle of 73-75 degrees is typical in road racing geometry, which brings the rider's weight forward and results in a more aggressive riding position.
- Steep head tube angle: A head tube angle of 71-72 degrees is common in road racing geometry, which provides quicker handling and more responsive steering.
- Short chainstays: Road racing geometry often features short chainstays, which result in a shorter wheelbase and more agility.
- Narrow handlebars: Narrow handlebars are common in road racing geometry, as they allow for more aerodynamic positioning and improved control.
Types of road bike frames:
- Road racing geometry: This type of geometry is designed for fast, efficient, and aggressive riding, typically used for road racing or high-speed, performance-oriented riding.
- Endurance/Gran Fondo geometry: This type of geometry is designed for long-distance comfort and stability, with a slightly taller head tube and shorter top tube than road racing geometry, which provides a more relaxed riding position.
- Triathlon/Time trial geometry: This type of geometry is designed for maximum aerodynamics and speed, with a steep seat tube angle and extended top tube, which allows for a more forward riding position.
- Gravel/Cyclocross geometry: This type of geometry is designed for off-road riding on a mix of terrain, with a more relaxed, stable, and upright riding position than road racing geometry, along with wider tires and lower gearing.
Mountain Bike Geometry
Mountain bike geometry refers to the frame geometry of bicycles that are designed for off-road riding and mountain biking. The focus of mountain bike geometry is to provide a balanced combination of stability, control, and handling for riding on challenging terrain.
There are several different types of mountain bike geometries, including cross-country, trail, enduro, and downhill, each with its own unique characteristics. Here are some general traits of mountain bike geometries:
- Slack head tube angle: A head tube angle of 68-69 degrees is common in mountain bike geometries, which provides more stability and a more relaxed, less twitchy ride.
- Long chainstays: Long chainstays are common in mountain bike geometries, which result in a longer wheelbase and improved stability, especially at high speeds.
- Wide handlebars: Wide handlebars are common in mountain bike geometries, which provide improved control and stability, especially in technical riding situations.
- Higher bottom bracket: A higher bottom bracket is common in mountain bike geometries, which provides improved clearance over obstacles and reduced risk of pedal strikes.
- Long top tube: A long top tube is common in mountain bike geometries, which provides a longer reach and improved stability, especially at high speeds.
It's important to note that these general traits can vary greatly depending on the type of mountain biking you plan to do and that choosing the right mountain bike geometry is essential for optimizing fit, comfort, and performance.
Types of mountain bike frames:
- Cross-country mountain bike geometry: This type of geometry is designed for racing or fast-paced riding on smoother terrain, with a lightweight and efficient design, steep head tube angle, and shorter travel suspension.
- Trail mountain bike geometry: This type of geometry is designed for all-around off-road riding on a mix of terrain, with a balanced combination of stability and agility, and mid-travel suspension.
- Enduro mountain bike geometry: This type of geometry is designed for more aggressive off-road riding on rough and steep terrain, with longer travel suspension, a slack head tube angle, and a low center of gravity.
- Downhill mountain bike geometry: This type of geometry is designed for high-speed and extreme off-road riding, with a long wheelbase, slack head tube angle, and full suspension.
Casual Riding Geometry
If you're in the market for a new bike or just starting to get serious about cycling, you've probably heard the term "casual riding geometry" thrown around. But what does it actually mean, and why should you care?
Simply put, casual riding geometry refers to the design of a bike's frame and components that are optimized for comfort and ease of use. This type of geometry is best suited for riders who prioritize a relaxed, upright riding position over speed and performance.
So what are the specific features of a bike with casual riding geometry? First and foremost, the frame will have a more upright and relaxed angle, which allows the rider to sit in a more comfortable and natural position. The handlebars will also be higher and wider, giving the rider more control and making it easier to maneuver the bike.
Other features of casual riding geometry may include wider tires, a softer saddle, and more relaxed gearing. These all work together to create a more comfortable and leisurely riding experience, which is perfect for cruising around town or exploring bike paths.
But why should you care about casual riding geometry? Well, for one thing, it can make cycling more accessible and enjoyable for people who might otherwise find it intimidating or uncomfortable. By prioritizing comfort and ease of use, casual riding geometry can help more people get on bikes and enjoy the many benefits of cycling.
Additionally, casual riding geometry can be a great choice for people who want to use their bike for commuting, running errands, or just getting around town. With a more comfortable and relaxed riding position, you'll be able to ride for longer periods of time without experiencing discomfort or pain.
IV. Factors to Consider in Choosing Bicycle Geometry
Body Size and Riding Style
When it comes to choosing the right bicycle geometry, two important factors to consider are body size and riding style. Proper bike fit is crucial for comfort, efficiency, and safety, and selecting the right bike geometry can help ensure a comfortable and enjoyable ride.
One of the most important factors to consider when selecting the right bike geometry is body size. A bike that is too small or too large can cause discomfort, pain, and even injury. Here are some key measurements to consider when choosing the right bike size:
- Inseam length: This is the distance from your crotch to the floor while standing in bare feet. It is an important measurement for determining the appropriate frame size.
- Height: Your height can also play a role in selecting the right bike size. Taller riders may prefer a larger frame size, while shorter riders may prefer a smaller frame size.
- Reach: The distance from the saddle to the handlebars is an important consideration for finding the right bike fit. Riders with longer arms may prefer a longer reach, while those with shorter arms may prefer a shorter reach.
Another important factor to consider when selecting the right bike geometry is riding style. Different styles of riding require different bike geometries to optimize performance and comfort. Here are some examples:
- Road bikes: These bikes are designed for speed and efficiency on paved roads. They typically have a more aggressive geometry with a longer reach and lower handlebars.
- Mountain bikes: These bikes are designed for off-road adventures on rugged terrain. They typically have a more upright geometry with a shorter reach and higher handlebars for better control on technical trails.
- Hybrid bikes: These bikes are designed for a mix of on-road and off-road riding. They typically have a more relaxed geometry with a shorter reach and higher handlebars for comfort and versatility.
- Touring bikes: These bikes are designed for long-distance touring and have a more relaxed geometry with a longer wheelbase for stability and comfort over long distances.
In addition to these general styles, there are also variations within each category that can further tailor the geometry to specific rider preferences.
Riding Goals and Preferences
When it comes to choosing the right bicycle geometry, another important factor to consider is your riding goals and preferences. Different riders have different priorities when it comes to bike geometry, and selecting the right geometry can help ensure a comfortable and enjoyable ride that meets your specific needs.
Here are some factors to consider when selecting the right bike geometry based on your riding goals and preferences:
- Comfort: If comfort is your top priority, consider a bike with a more relaxed geometry. This might mean a shorter reach, a higher handlebar position, and a more upright riding position. A comfortable bike will allow you to ride longer distances with less fatigue and discomfort.
- Speed: If speed is your top priority, consider a bike with a more aggressive geometry. This might mean a longer reach, lower handlebars, and a more aerodynamic riding position. A bike with a more aggressive geometry will help you cut through the wind and ride faster on flat roads and climbs.
- Handling: If you prioritize handling and maneuverability, consider a bike with a shorter wheelbase and steeper head tube angle. This will make the bike more responsive and easier to maneuver through tight corners and technical terrain. On the other hand, if stability is more important to you, consider a bike with a longer wheelbase and shallower head tube angle.
- Terrain: The type of terrain you plan to ride on can also influence your choice of bike geometry. For example, if you plan to ride on steep mountain trails, a bike with a slack head tube angle and longer wheelbase will provide better stability on steep descents. On the other hand, if you plan to ride on smooth, flat roads, a bike with a steeper head tube angle and shorter wheelbase will be more efficient and faster.
- Fit: Ultimately, the right bike geometry for you will depend on your body size, flexibility, and riding preferences. A professional bike fit can help ensure that you select a bike with the right geometry for your body and riding style. Factors such as saddle height, handlebar reach, and stem length can all be adjusted to create a perfect fit that is comfortable and efficient.
V. Conclusion
In conclusion, bicycle geometry plays a crucial role in determining the comfort, efficiency, and performance of a bike. The key factors to consider when selecting the right bike geometry include body size, riding style, riding goals, terrain, and fit. By taking these factors into account, riders can select a bike with the right geometry that will provide a comfortable and enjoyable riding experience. Whether you're a recreational rider, a competitive racer, or a long-distance tourer, selecting the right bike geometry can help you ride more comfortably, efficiently, and safely.
It's also important to note that there is no "one size fits all" solution when it comes to bike geometry. Each rider is unique and requires a bike that fits their individual body size, flexibility, and riding style. Therefore, it's recommended to get a professional bike fit to ensure that your bike is set up correctly and provides the most efficient and comfortable ride possible.